In today's interconnected world, managing IoT devices behind a firewall is crucial for maintaining network security and ensuring seamless device functionality. As the number of IoT devices continues to grow, businesses and individuals face increasing challenges in securing their networks while maximizing the benefits of IoT technology. Proper management of these devices is essential for protecting sensitive data and preventing unauthorized access.
IoT devices have revolutionized the way we interact with technology, offering innovative solutions across various industries. However, the integration of these devices into existing networks introduces new security concerns. Firewalls play a vital role in safeguarding networks from external threats, but managing IoT devices behind them requires a strategic approach.
This article provides a comprehensive guide on how to manage IoT devices behind a firewall effectively. We'll explore key strategies, tools, and best practices to ensure your network remains secure while optimizing IoT device performance. Whether you're a network administrator, IT professional, or business owner, this guide will equip you with the knowledge needed to address the unique challenges of IoT device management.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to IoT Device Management
- Understanding Firewalls and Their Role
- Challenges in Managing IoT Devices Behind a Firewall
- Strategies for Managing IoT Devices
- Tools for Effective IoT Device Management
- Enhancing Security Measures
- Implementing Network Segmentation
- Best Practices for IoT Device Management
- Real-World Case Studies
- Future Trends in IoT Device Management
Introduction to IoT Device Management
Managing IoT devices behind a firewall involves several critical steps to ensure both security and functionality. IoT devices operate on networks that require robust firewalls to filter incoming and outgoing traffic. Proper management includes monitoring device activity, updating firmware, and configuring firewall rules to accommodate IoT-specific needs.
Why is IoT Device Management Important?
IoT devices often lack the same level of security as traditional computing devices. This makes them vulnerable to attacks if not properly managed. Effective management helps mitigate risks and ensures devices operate efficiently within the network. Key aspects include:
- Monitoring device behavior for anomalies.
- Regularly updating firmware to patch vulnerabilities.
- Configuring firewall settings to allow necessary traffic.
Key Challenges in IoT Device Management
One of the primary challenges is balancing security with usability. Firewalls must be configured to allow IoT devices to communicate with external services without compromising network security. Additionally, managing a large number of devices can be resource-intensive, requiring scalable solutions.
Understanding Firewalls and Their Role
Firewalls act as a barrier between internal networks and external threats. They filter traffic based on predefined rules, ensuring only authorized data passes through. For IoT devices, firewalls must be configured to recognize and manage device-specific traffic patterns.
Types of Firewalls
There are several types of firewalls, each suited for different use cases:
- Packet Filtering Firewalls: Analyze individual packets for specific criteria.
- Stateful Inspection Firewalls: Track active connections and context.
- Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFW): Incorporate advanced features like intrusion prevention.
Firewall Configuration for IoT Devices
Configuring firewalls for IoT devices involves setting up rules that allow necessary communication while blocking unauthorized access. This includes defining ports, protocols, and IP addresses that IoT devices use.
Challenges in Managing IoT Devices Behind a Firewall
Managing IoT devices behind a firewall presents several challenges. These devices often use proprietary protocols and may not adhere to standard security practices. Additionally, the sheer number of devices can overwhelm traditional firewall configurations.
Device Diversity
IoT devices come in various forms, each with unique communication requirements. Managing this diversity requires flexible firewall rules and policies that can adapt to different device types.
Scalability Issues
As the number of IoT devices grows, firewalls must scale to handle increased traffic. This requires robust hardware and software solutions capable of managing large-scale networks.
Strategies for Managing IoT Devices
Implementing effective strategies is essential for managing IoT devices behind a firewall. These strategies focus on enhancing security, improving device performance, and simplifying management processes.
Centralized Management
Using a centralized management platform allows administrators to monitor and control all IoT devices from a single interface. This simplifies the management process and ensures consistent security policies across the network.
Automated Updates
Enabling automated firmware updates ensures devices remain secure against emerging threats. Regular updates also improve device performance and functionality.
Tools for Effective IoT Device Management
Several tools are available to assist in managing IoT devices behind a firewall. These tools provide features such as device monitoring, traffic analysis, and automated rule configuration.
Popular IoT Management Tools
- Microsoft Azure IoT Hub: Offers comprehensive device management and monitoring capabilities.
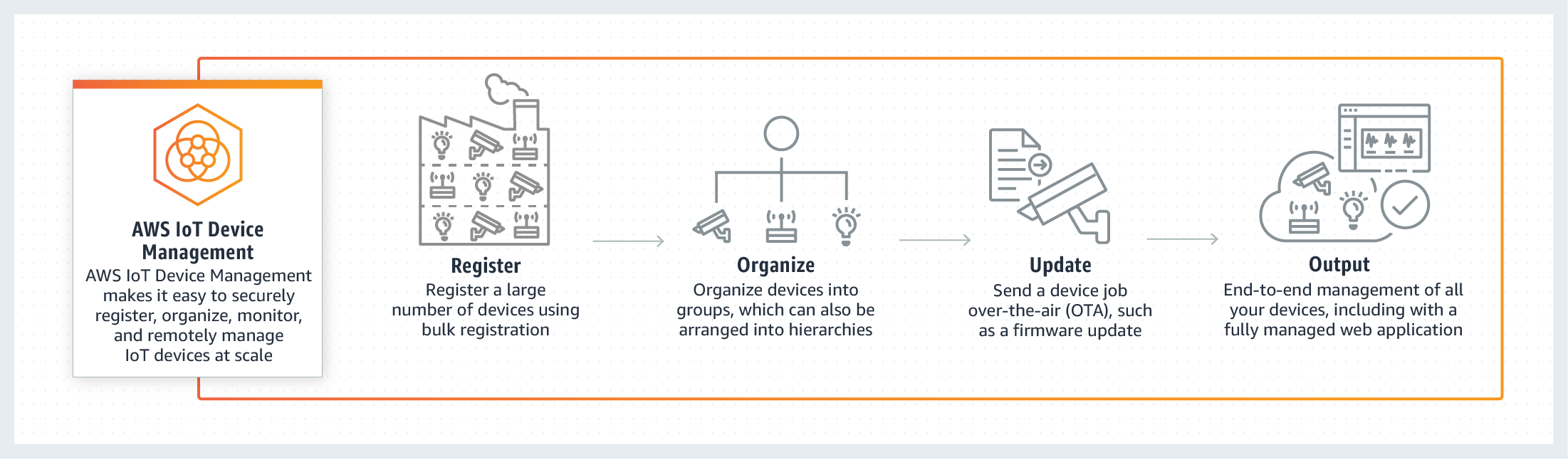
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) IoT Core: Provides scalable solutions for managing large fleets of IoT devices.
- Palo Alto Networks: Offers advanced firewall solutions tailored for IoT environments.
Choosing the Right Tool
Selecting the appropriate tool depends on specific network requirements, device types, and budget constraints. Evaluating these factors ensures the chosen solution meets all necessary criteria.
Enhancing Security Measures
Security is a top priority when managing IoT devices behind a firewall. Implementing robust security measures helps protect against unauthorized access and data breaches.
Encryption and Authentication
Using encryption and strong authentication protocols ensures data transmitted between IoT devices and external services remains secure. This includes implementing TLS/SSL for data encryption and multi-factor authentication for device access.
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
Deploying IDS solutions helps detect and respond to potential threats in real-time. These systems monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and alert administrators of potential security breaches.
Implementing Network Segmentation
Network segmentation involves dividing a network into smaller, isolated segments. This approach enhances security by limiting the spread of potential threats and simplifying device management.
Benefits of Network Segmentation
- Reduces attack surface by isolating IoT devices from critical systems.
- Improves network performance by reducing congestion.
- Simplifies management by grouping similar devices together.
Segmentation Strategies
Effective segmentation strategies include using VLANs, subnets, and firewall rules to create distinct network segments for IoT devices. This ensures devices operate securely without affecting the rest of the network.
Best Practices for IoT Device Management
Adopting best practices is crucial for successful IoT device management behind a firewall. These practices ensure devices remain secure and function optimally within the network.
Regular Audits and Assessments
Conducting regular audits and assessments helps identify potential vulnerabilities and areas for improvement. This includes reviewing firewall rules, monitoring device activity, and updating security policies as needed.
Employee Training and Awareness
Training employees on IoT security best practices and raising awareness about potential threats is essential for maintaining a secure network environment.
Real-World Case Studies
Examining real-world case studies provides valuable insights into successful IoT device management strategies. These examples highlight the challenges faced and solutions implemented by organizations in various industries.
Case Study 1: Smart Manufacturing Facility
A manufacturing facility implemented a centralized management system to oversee hundreds of IoT devices. By configuring firewalls to allow specific traffic patterns and segmenting the network, they successfully enhanced security while improving operational efficiency.
Case Study 2: Healthcare Provider
A healthcare provider deployed advanced firewall solutions to manage IoT medical devices. This ensured patient data remained secure while enabling seamless device communication with external systems.
Future Trends in IoT Device Management
The future of IoT device management is shaped by emerging technologies and evolving security standards. Key trends include the adoption of AI-driven solutions, increased focus on privacy, and the development of standardized protocols.
Artificial Intelligence in IoT Management
AI technologies are increasingly being used to automate device management tasks and enhance security. Machine learning algorithms analyze device behavior to detect anomalies and predict potential threats.
Standardization and Interoperability
Efforts to standardize IoT protocols and improve device interoperability will simplify management and increase adoption. These developments will enable more efficient and secure IoT device management across diverse networks.
Conclusion
Managing IoT devices behind a firewall is a complex but essential task for maintaining network security and optimizing device performance. By implementing effective strategies, leveraging advanced tools, and adopting best practices, organizations can successfully address the challenges associated with IoT device management. As technology continues to evolve, staying informed about emerging trends and solutions will ensure networks remain secure and resilient.
We encourage readers to share their experiences and insights in the comments section below. Additionally, explore other articles on our site for more information on IoT security and network management. Together, we can build a safer and more connected digital future.